Why a Fiber Optic Security System Enhances Your Property’s Safety and Surveillance
Wiki Article
Why Fiber Optic Protection Systems Are the Future of Security
The shift to fiber optic protection systems notes a significant advancement in the realm of protection, driven by their exceptional information transmission capacities and strength to outside disturbances. As the landscape of safety progresses together with arising innovations such as AI and IoT, the possibility for fiber optics to boost and redefine safety and security frameworks ends up being progressively obvious.Advantages of Fiber Optic Systems
Among the key benefits of fiber optic systems is their exceptional data transfer ability, which promotes the transmission of big volumes of data over cross countries without substantial loss. This particular is specifically valuable for protection applications that require the constant tracking and transfer of high-def video feeds, sensing unit information, and other important info. Optical fiber can accommodate the growing needs of modern-day protection systems, making sure that data stays undamaged and reliable.In addition, fiber optic wires are much less prone to electromagnetic interference, which can be a substantial problem in settings with different digital gadgets. This resistance enhances the integrity of the data being transferred, consequently lessening the danger of data breaches or system failures. Fiber optic systems are inherently a lot more safe than typical copper cable televisions, as touching into a fiber optic line without detection is exceedingly tough.
The durability of fiber optic wires likewise adds to their charm. They are immune to environmental elements such as dampness and temperature changes, reducing maintenance expenses and increasing system durability. On the whole, these advantages placement fiber optic systems as a robust and effective selection for modern-day security facilities, making certain dependable and safe and secure information transmission.
Enhanced Data Transmission Speed
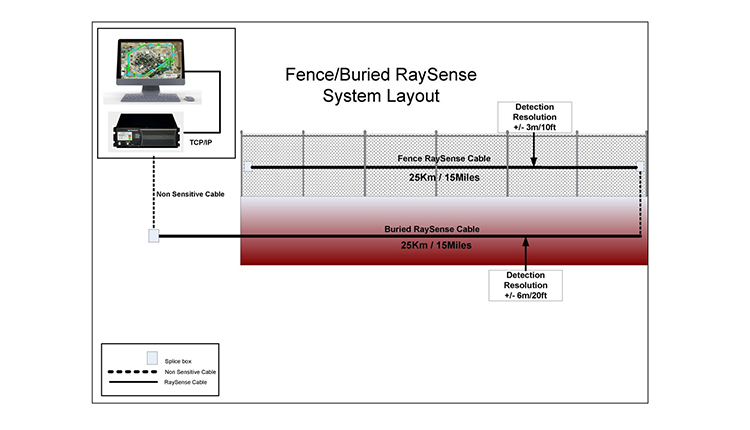
The ability to transfer huge amounts of information quickly promotes the smooth combination of high-definition video feeds and advanced analytics. Safety and security systems can now refine and examine info in real-time, improving feedback times and situational recognition. In addition, fiber optic links support longer transmission ranges without degradation of signal top quality, making them excellent for extensive security networks.
The increased speed of fiber optic systems not just boosts the effectiveness of safety and security procedures however also decreases latency. This is particularly important in critical circumstances where prompt decision-making can avoid security violations or mitigate possible threats. As companies remain to focus on security and effectiveness, the need for fast and trusted information transmission will definitely strengthen fiber optic systems as a cornerstone of modern-day safety facilities.
Resistance to Interference
Fiber optic safety and security systems constantly show remarkable resistance to electro-magnetic interference, a critical benefit in settings susceptible to digital sound. Unlike typical copper cables, which can be adversely impacted by electro-magnetic areas, superhigh frequency disturbance, and other types of electric disruption, fiber optic cables use light to transmit information. This inherent residential or commercial property makes sure that the signals continue to be clear and unaltered, regardless of surrounding digital activity.The usage of glass or plastic fibers in fiber optic modern technology produces a barrier against interference, permitting reputable data transmission also in difficult scenarios such as industrial facilities, metropolitan areas with high digital traffic, or locations near radio towers. This characteristic significantly minimizes the possibility of signal degradation or loss, making fiber optic systems particularly appropriate for security applications where honesty and accuracy of information are critical.
Additionally, this resistance to interference improves the total performance and reliability of security systems, ensuring that monitoring and alert systems function flawlessly. In a globe where protection is increasingly threatened by sophisticated technologies, the strength of fiber optic systems attracts attention as a critical function, strengthening their status as a crucial component of contemporary safety framework.
Cost-Effectiveness With Time
Significant expense financial savings can be accomplished with time with the implementation of fiber optic security systems. While the initial investment might seem greater compared to typical copper-based systems, the lasting economic advantages come to be obvious via reduced operational and maintenance expenses (fiber security). Fiber optic cables are inherently much more durable and less prone to environmental elements, which converts to lower replacement and fixing expenses over their life expectancyIn addition, fiber optic systems call for less power to run, which additionally lowers power costs. Enhanced information transmission abilities permit for fewer repeaters and amplifiers, reducing tools financial investment and streamlining installation procedures. The scalability of these systems likewise adds to cost-effectiveness, as organizations can expand their safety and security facilities without sustaining substantial added expenses.
One more element to take into consideration is the boosted performance in monitoring and feedback abilities that fiber optics provide. Improved real-time information transmission can cause quicker incident action times, potentially mitigating losses and responsibilities connected with protection violations. Altogether, the long-lasting benefits of fiber optic safety systems not just warrant the first expense but find here likewise position them as an economically prudent choice for companies looking for robust security options.

Future Developments in Security
Advancing technologies are set to revolutionize safety systems, incorporating artificial knowledge (AI) and artificial intelligence to enhance danger discovery and action capabilities. These innovations will enable safety and security systems to analyze substantial quantities of information in real-time, determining patterns and abnormalities that suggest potential hazards. This proactive strategy will allow quicker decision-making and much more reliable occurrence reactions.In addition, the unification of the Net of Things (IoT) is pop over to this site leading the way for interconnected safety tools, providing thorough security and tracking. Smart sensors can pass on info about ecological adjustments, while automated informs can inform safety personnel promptly of questionable activities.
In addition, the evolution of biometric modern technologies will better bolster protection mechanisms. Facial acknowledgment, fingerprint scanning, and retina recognition are ending up being extra sophisticated, offering layers of verification that are challenging to bypass.
Conclusion
Finally, fiber optic safety systems stand for a substantial improvement in defense innovation, supplying unrivaled data transmission rate, resistance to electro-magnetic disturbance, and lasting cost-effectiveness. As the demand for advanced protection solutions proceeds to grow, the combination of optical fiber with arising technologies such as AI, IoT, and biometrics will even more improve protection frameworks (fiber security). The mix of these innovations will guarantee a much more protected and responsive atmosphere, see post solidifying fiber optics as a foundation of future safety and security systemsReport this wiki page